Reference points are benchmarks used to compare the current status of a fishery management system against a desirable (or undesirable) state. When ingrained in the agreed management objectives for a fishery, they can be used to assess progress toward meeting those objectives. Check out our resources reference points to learn about the different types of reference points and considerations when choosing candidate reference points.
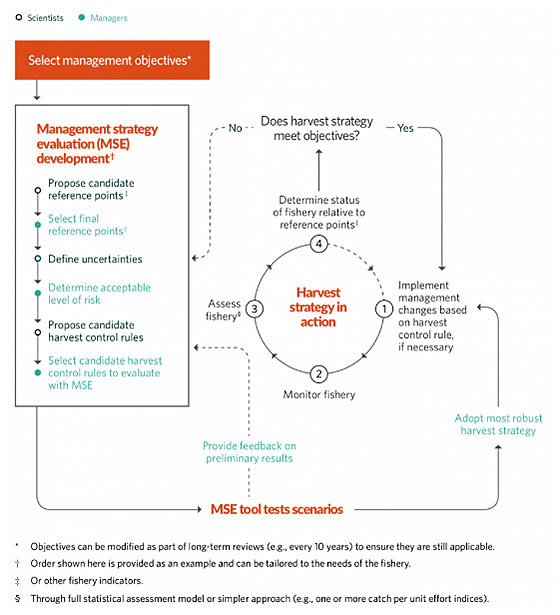
Although management bodies name and define them slightly differently, all harvest strategies include these basic elements: management objectives; a monitoring program; indicators of the fishery’s status and population health, with associated reference points; a method to assess those indicators; and harvest control rules that set fishing opportunities, which could include catch and size limits, depending on the value of key indicators relative to the reference points.
In most regions, “management procedure” and “harvest strategy” are used synonymously. However, in some regions, like the western Pacific, a management procedure is considered a type of harvest strategy. In that case, the distinction is that a “harvest strategy” is a more general management framework, whereas each component of a “management procedure” is formally specified, and the combination of monitoring data, analysis method, and harvest control rule has been simulation tested using MSE to demonstrate adequately robust performance in the face of plausible uncertainties about stock and fishery dynamics. It is this definition that HarvestStrategies.org uses for “management procedure” and “harvest strategy.”
Effective long-term management of the world’s fish stocks requires science, stakeholder engagement, and advanced planning. Harvest strategies can help enable effective fisheries management by:
Check out our animation, “Fishing for the Future: The Case for Harvest Strategies,” and our blogs to learn more about the benefits of harvest strategies.
Robust harvest strategies, before they are implemented, are tested through a scientific process called management strategy evaluation (MSE), used to simulate the workings of a fisheries system and test whether potential harvest strategies can achieve the pre-agreed management objectives. MSE helps to identify the harvest strategy likely to perform best, regardless of uncertainty, and balance trade-offs amid competing management objectives. Because MSE is so fundamental to harvest strategies, some consider the term to encompass the process of harvest strategy development itself. Explore our data visualization tools for MSE results, and check out our animation to learn more about MSE.
In most regions, “management procedure” and “harvest strategy” are used synonymously. However, in some regions, like the western Pacific, a management procedure is considered a type of harvest strategy. In that case, the distinction is that a “harvest strategy” is a more general management framework, whereas each component of a “management procedure” is formally specified, and the combination of monitoring data, analysis method, and harvest control rule has been simulation tested using MSE to demonstrate adequately robust performance in the face of plausible uncertainties about stock and fishery dynamics. It is this definition that HarvestStrategies.org uses for “management procedure” and “harvest strategy.”
A harvest strategy, also known as a management procedure, is a pre-agreed framework for making fisheries management decisions (such as catch or effort limits) to achieve a long-term vision for the fish and fishery. Before they are implemented, robust harvest strategies are tested through a process that involves fishery scientists, managers, and other stakeholders, which is called management strategy evaluation (MSE).
Check out our resources to learn more about the basic elements of a harvest strategy and how the process works.
Most content on HarvestStrategies.Org is available in English, French, and Spanish. Certain resources may be available in additional languages (e.g., Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Chinese, Thai, German, Portuguese, Italian. If there is a particular language in which you’d like a specific product, please connect with us!
Harvest strategies contribute significantly to the economic viability of fisheries by promoting long-term sustainability and stability, which in turn helps bolster fishing opportunities and market confidence. Harvest strategies provide the fishing industry with the stability needed for business planning and investment by ensuring that management decisions are predictable and based on data-driven benchmarks. This predictability helps mitigate risks associated with overfishing or sudden regulatory changes and enhances access to new markets through sustainable seafood certifications.
Fisheries that follow scientifically sound harvest strategies are more likely to meet the requirements for eco-labeling programs such as the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), opening doors to higher-value markets and consumer demand for sustainably sourced products. Also, maintaining target abundance levels ensures healthy fish populations, benefiting the ecosystem and fishery. Healthy stocks translate to more consistent yields, reducing variability in catches and improving the long-term profitability of the industry.
Although different management bodies may take different approaches, harvest strategies are all developed using MSE and generally follow this development process:
 Check out our animation that explains harvest strategies, including how they are developed to achieve a long-term vision for a stock and the fisheries that target it.
Check out our animation that explains harvest strategies, including how they are developed to achieve a long-term vision for a stock and the fisheries that target it.